
Welcome to
My Aviary
'Welcome to my Aviary', shortened to 'WtmA' or 'My Aviary', is a bird breeding game revolving around fictional parrot species loosely based on real bird genetics.Breed your favourite parrots, build your perfect aviary, collect birds of beautiful colours, get in touch with the community, and so much more!

Welcome to my Aviary
Basic information about the game and how everything works. Here you will also find a list of rules, guides and information on how to join!
WTMA Bird Species
Detailed profiles about all the fictional bird species WtmA has to offer! This is the place to go for anything you want to know about the birds.


WTMA Bird Genetics
An in-depth guide to the basics of genetics and all the fictional genetics applied to WtmA's bird species! Don't worry, Gene Staff are ready in the server to help.
Join our Discord server for updates about the game and be the first to join the game!
WtmA Info
Here you can find the rules, essential information and useful links. If you're done reading, please check out the Game Guide!Use the buttons below to quickly navigate through this page.
Rules
This section includes some rules and terms to follow and keep in mind when playing the game. More may be added in the future.
OWNERSHIP
Though you may 'own' several birds in-game, the sprites (IMAGES) are owned by the game and its creator, Tanimtoo. You are allowed to download the images and use them casually (e.g. send one in Discord to show a bird you're talking about) but you may not post them (e.g. upload to Toyhouse as original character or a character's pet).
Tanimtoo claims no ownership over the genetics as many are based on IRL genetics or suggestions from the community. Please do contact Tanimtoo if you wish to use WtmA's genetics for other projects.
Even though the bird species are based on real genera, they are still designed by Tanimtoo. Please do not directly copy any of these birds' designs for your own use.
YOUR DATA
WtmA has no account system, we do not collect any data such as emails or passwords (not even cookies lol). The only 'data' we use, is the nickname you personally submit to us and your Discord ID. These are used on the bird database to put your name on the birds you own and your inventory.
If you wish to leave the game, your birds will be deleted or go up for rehoming and your inventory will be destroyed. Your nickname may remain in transfer logs unless you specifically state you want them removed to.
That being said, WtmA has the right to remove your 'data' as well. If you banned from the game, for example, you will loose your birds and items the same way as anyone would when leaving the game.
Before you Join
'Welcome to my Aviary' is a Discord-based bird breeding game. If you're familiar with sites such as Wolvden, Lioden, Flight Rising, Pure Felinity or Howrse, you may have an idea of what vibe we're trying to achieve!WtmA can be played at any time as much or as little as you want. While events (e.g. auctions, shows) may be available for a limited amount of time, they'll return eventually. You can freely take a 4 week long vacation and all your birds will be ready for you like you left them. WtmA is not an ARPG ('art roleplaying game') and doesn't require you to draw anything or submit any other creative works to participate.We rely on active staff members rather than an automated system. Game systems are done through submitting forms and alerting specialized staff teams. This means it may take a while for changes to be made (less than 24 hours) but also makes the game a lot more interactive and personal. The staff team are also your fellow players!There's no commitment. You are free to be inactive, go on a hiatus or decide to leave the game completely. We do value communication. If you plan on leaving the game, please just let us know. If you leave the server or delete your account, we may delete your data and/or transfer your birds after a certain amount of time.Sounds good? You're in? Go ahead and read the Startup Guide on how to join!
WtmA Guide
Here you can find guides on how to participate in WtmA. All game systems are explained in the guides. If you're new, check out the Startup Guide to get yourself started!Please use the buttons below to quickly navigate through this page.
Startup Guide: Joining the Game
To join the game, you need to join the Discord server. Once you're in the Discord server, read the rules and click on the checkmark in the channel to recive the @Newbie role; giving you access to more of the server.Once you've gained the @Newbie role, you can head over to the #sign-up channel. Follow the instructions in that channel and fill in the form. It may take up to 24 hours for staff to get back to you, please be patient!When your application is accepted, a staff member will create a thread for you in the #tutorial channel. This staff member will be giving you a 'tutorial' where they inform you of key aspects of the game and get you set up with your very first bird!
Guide: Aviaries, Cages & Locations
Aviaries, cages and locations will be part of a future update and are not a feature just yet, sorry!
Guide: Shopping & Currency
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Guide: Items & Inventory
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Guide: Keeping your Birds
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Guide: Breeding your Birds
You will need the following: 2 birds of the same species and opposite sex, nesting material and suitable feed.
When you have all the above things (you can find these items in the shop, ask staff if you're not sure which are suitable options), you copy and fill in the form found in the #breeding channel. Below is a table with a breakdown of the form!
If all the information is correct, staff will re-post your message and attach a thread to the bottom. All further gameplay and updates will take place in this thread.
Staff will let you know the amount of eggs in the clutch and set a timer until they're done.
When the eggs have hatched, staff will redirect you to the #chick-care channel, where your journey of raising the young chicks will start. You can find more about this in the Raising Guide.
| Form | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ring cock | ARAT-0012-ABC-19 | The full ringnumber of the male bird |
| Ring hen | ARAT-0068-XYZ-21 | The full ringnumber of the female bird |
| Ring ID | ABC | Breeder Ring ID. This only applies to registered breeders, if you are a hobby breeder, you put down '000' |
| Items | 1x Nesting Material | Non-feed items used for breeding |
| Feed | 1x [Feed TBA] | Feed used for breeding |
Guide: Raising Young Birds
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Guide: Transfer, Sale & Release
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Guide: WtmA Bird Shows
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Guide: WtmA Auctions
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Bird Species
Below is a list of every single bird that can be found in WtmA! The list is sorted on 'categories' such as macaws, cockatoos and parakeets! Other parrots are sorted on size (large, medium, small).Click the bird's icon to view all of its information!
Macaws - Ara
Cockatoos - Genus
Parakeets - Bolborhynchus
Lories - Genus
Large Parrots - Genus
Medium Parrots - Poicephalus
Small Parrots - Genus
Non-parrots - Genus
Black-capped Macaw
(Ara Atricapilla)
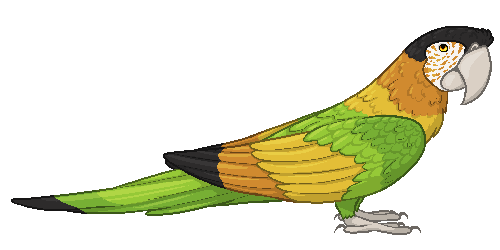
[Little basic info about the bird.]
Essential Info
| Sex Determination | No sexual dimorphism; DNA test only |
| Category | Macaw, large |
| Average Lifespan | 30-50 years |
| Average Price | $1200 |
| Database | Species page, all registered birds |
Description
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Behaviour
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Habitat
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Breeding
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Genetics
Information on genetics and reference material will be added once more variants and mutations are discovered. Please check back leter.
TBN
(Bolborhynchus scintilla)

[Little basic info about the bird.]
Essential Info
| Sex Determination | No sexual dimorphism; DNA test only |
| Category | Parakeet, small |
| Average Lifespan | 10 years |
| Average Price | $250 |
| Database | Species page, all registered birds |
Description
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Behaviour
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Habitat
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Breeding
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Genetics
Information on genetics and reference material will be added once more variants and mutations are discovered. Please check back leter.
Great Lakes Parrot
(Poicephalus magnalacus)

[Little basic info about the bird.]
Essential Info
| Sex Determination | No sexual dimorphism; DNA test only |
| Category | Parrot, medium |
| Average Lifespan | 20-30 years |
| Average Price | $600 |
| Database | Species page, all registered birds |
Description
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Behaviour
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Habitat
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Breeding
Sorry, this part is still under construction, please check back later!
Genetics
Information on genetics and reference material will be added once more variants and mutations are discovered. Please check back leter.
Genetics
Click on 'The Basics' below if you are new to genetics. Here you will learn terms, how genes work, how to calculate offspring, etc.
Already know the basics? Then you can immediately move on to 'WtmA Genetics' for an overview and guide to all genes that will be used in the game.We've got Gene Staff in the Discord server ready to answer any questions you have!These pages are both work in progress, the information on them is not complete nor final. Please check back later.
Genetics: The Basics
Sorry!Under construction...
Terminology
Here is a list of terms used surrounding genetics and what they mean. To keep this list short, not all meanings include every possible situation.
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Genotype | - The genetic code that makes up the bird, written using a string of alleles. |
| Phenotype | - The physical appearance of the bird as decided by the genotype. |
| Allele | - The letters that indicate genes and make up the genetic code of the bird. |
| Locus | - The place the alleles are expressed or the category in which alleles are grouped. |
| Dominant | - Only one of these alleles needs to be present for the bird to present the gene. It is 'dominant' over the other genes. |
| Recessive | - Two of these alleles need to be present for the bird to present the gene. It is 'recessive' to the dominant genes. |
| Co-dominant | - Two co-dominant genes create a phenotype not achievable by homozygous alleles. |
| Homozygous | - Both alleles on the locus are the same. For example; AA, bb, etc. |
| Heterozygous | - The two alleles on the locus are not the same. For example; Aa, Bb, etc. |
| Wild type | - The original colouring of a bird without any mutations which you can find in the wild. |
| Split | - When a bird has a recessive gene that doesn't show in the phenotype, they are 'split to' that gene. |
Alleles and Loci
As stated in the terminoloy, alleles are "the letters that indicate genes and make up the genetic code of the bird" and a locus is "the place the alleles are expressed or the category in which alleles are grouped," but what does this mean?Every gene has a unique letter or two associated with it, which are the alleles. There are a lot of genes, so when making a list or table it will get very hard to say "female, homozygous lutino, heterozygous wild type and turquoise, etc." and it's easier being able to say "ZW LL Bbt" instead.Biologically speaking, a locus is a specified section of a chromosome in DNA where a selection of genes are located. To simplify it, you can view a locus as a category for genes. The Lutino locus has two genes; wild type and lutino, for example.
Offspring
When two birds breed, their offspring will inherit half of each their genes. Each parent passes on one random allele of each pair to their young.
To visualize offspring possibilities, you can put the alleles in a table. In the top row you put the allels of one parent and in the left column the other. Then you combine the two alleles to give 4 possible options for chicks. Sometimes the same allele combination pops up multiple times, this means that combination will be more likely in chicks.In this example we'll show the outcome for the Blue locus. A wild type hen (split to violet) is indicated by yellow. A blue cock (split to turquoise) is indicated by blue.
| B | bv | |
| b | Bb | bbv |
| bt | Bbt | btbv |
Here is an example table following the lutino gene. Lutino is sex-linked, attached to the Z chromosome, hence why there are different possibilities depending on the sex of the chicks. Note that these are not two parents, these simply note down all the possible combinations two birds may form and all chicks that may come out of that combination.
| ZW L (wild hen) | ZW l (lutino hen) | |
| ZZ LL (wild cock) | 50% ZZ LL (wild cock) 50% ZW L (wild hen) | 50% ZZ Ll (lime cock) 50% ZW L (wild hen) |
| ZZ Ll (lime cock) | 25% ZZ LL (wild cock) 25% ZZ Ll (lime cock) 25% ZW L (wild hen) 25% ZW l (lutino hen) | 25% ZZ Ll (lime cock) 25% ZZ ll (lutino cock) 25% ZW L (wild hen) 25% ZW l (lutino hen) |
| ZZ ll (lutino cock) | 50% ZZ Ll (lime cock) 50% ZW l (lutino hen) | 50% ZZ ll (lutino cock) 50% ZW l (lutinohen) |
Genetics: WtmA Guide
On this page you can find all colour mutation genes that may be present in any of WtmA's parrot species.Because all parrots have a different wild type, the same gene will have a different outcome on every bird. For species-specific visuals you can visit the species' page!This page only displays genes present in the Psittaciformes (parrots) order. The few non-parrots WtmA has to offer will have their genetic information displayed on their species page.
OVERVIEW
| # | Locus | Allele | Phenotype | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lutino | L | wild type | sex-linked, co-dominance |
| l | lutino | sex-linked, co-dominance | ||
| 2 | Blue | B | wild type | |
| b | blue | |||
| bt | turquoise | |||
| bv | violet | |||
| 3 | Pastel | P | wild type | |
| p | pastel | |||
| 4 | Opaline | Op | wild type | sex-linked, co-dominance |
| op | opaline | sex-linked, co-dominance | ||
| 5 | Pied | Sh | heavy pied | white, more pied |
| sl | light pied | yellow, less pied | ||
| s | wild type | no change | ||
| 6 | Iridesence | C | wild type | |
| ci | iridescent |
Sex Chromosomes
These aren't genes but should be noted down for reference as they are very important!The last pair of a bird's chromosomes are called the Sex Chromosomes, they determine the sex of the bird. Unlike humans and many other animals (cats, dogs, horses, etc.) who have XY chromosomes, birds have ZW chromosomes.
| ZW | female | hens pass on a Z or a W chromosome to their offspring. this way she determines the sex of her young |
| ZZ | male | cocks pass on either of their Z-chromosomes to their offspring. |
Lutino
Lutino is a sex-linked gene that removes black and blue pigments from the bird. This leaves the bird with only yellows and reds.This sex-linked gene is attached to the Z chromosome. Meaning that hens (ZW) have one lutino allele while cocks (ZZ) have two alleles. These two can be homozygous (LL or ll) or heterozygous (Ll).When you've got a heterozygous male carrying both lutino and wild type, it ends up removing some black and blue pigments - but not all, it leaves a bit of blue and gray. This often leaves birds with a greenish-yellow colour. We call this lime.
| Allele | Phenotype | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| L | wild type | no change |
| l | lutino | removes black and blue pigments |
| LL | wild type | either sex; ZLW, ZLZL |
| Ll | lime | male birds only; ZLZl |
| ll | lutino | either sex; ZlW, ZlZl |
When talking about only this gene, it can be written together with the sex chromosomes, ZLW or ZlW for hens and ZLZL, ZLZl or ZlZl for cocks. But when writing out the lutino gene for the full genetic code it should be written separately (ZW L, ZW l, ZZ LL, ZZ Ll, ZZ ll) to not get cluttered with other sex-linked genes.
Blue
Blue is a gene that removes red and yellow pigments from the bird. This leaves the bird with only blues and blacks.Two of the genes within the Blue locus don't remove all the red and yellow. These are turquoise and violet. Turquoise leaves a little yellow while violet leaves a little red. In combination with the most likely blue colour, turquoise turns most birds greenish-blue and violet turns most birds a rich indigo-blue or sometimes even purple.The list below is in order of dominance. B > b > bt > bv
| Allele | Phenotype | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| B | wild type | no changes |
| b | blue | all red and yellow removed |
| bt | turquoise | all red and some yellow removed |
| bv | violet | all yellow and some red removed |
| B- | wild type | BB, Bb, Bbt, Bbv |
| b- | blue | bb, bbt, bbv |
| bt- | turquoise | btbt, btbv |
| bv- | violet | bvbv |
A note about the Blue and Lutino loci: These two loci are the main loci to alter a bird's colour. Note that they only remove pigment. This means a bird who's wild type is completely red will never turn blue with the Blue gene. The combination of the lutino gene and the blue gene will leave a bird completely white.
Pastel
Pastel is a gene that dilutes the pigment throughout the entire bird. This gives the bird a lighter and more 'pastel' appearance. In some cases, black parts of a bird may turn blue-ish when affected by the pastel gene. The list below is in order of dominance. P > p
| Allele | Phenotype | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| P | wild type | no change |
| p | pastel | dilutes pigment in the whole bird |
| P- | wild type | PP, Pp |
| p- | pastel | pp |
With the pastel gene certain birds may appear a blue pastel while they're turquoise/violet pastel or even give a near-white appearance to lighter coloured wild types or in the combination with other genes.
Opaline
Opaline, for some species known as Pearl, is an odd sex-linked gene that has a different effect on each species. The opaline gene relocates certain colours which can take form as spots on feathers, discoloured edges around feathers, enlarged colour patches, disappearance of colour and complete relocation of colour.
| Allele | Phenotype | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Op | wild type | no change |
| op | opaline | relocates colour |
| Op/Op | wild type | either sex; ZOpW, ZOpZOp |
| Op/op | wild type | male birds only; ZOpZop |
| op/op | opaline | either sex; ZopW, ZopZop |
When a bird is split to opaline, they will show as an opaline bird until their first molt, after which they will appear like a wild type instead. Because opaline is sex-linked, only cocks can be split to opaline.
Pied
The pied gene creates randomly placed patches with loss of pigment all over the bird. This often affects the flight feathers, shoulders and back, but otherwise appears all over the body.There are two types of pied; heavy pied and light pied. Heavy pied, sometimes referred to as white-pied, leaves more and bigger patches and removes all pigment. Light pied, sometimes referred to as yellow-pied, leaves less and smaller patches that removes most pigment except yellow.
| Allele | Phenotype | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sh | heavy pied | white, more pied |
| sl | light pied | yellow, less pied |
| s | wild type | no change |
| Sh/Sh | clear pied | white, 80-100% |
| Sh/sl | heavy pied | white, 60-80% |
| Sh/s | heavy pied | white, 40-60% |
| sl/sl | light pied | yellow, 20-40% |
| sl/s | light pied | yellow, 0-20% |
| s/s | wild type | no change |
Note that the percentages shown above are average ranges observed by birds with those genetics. A homozygous heavy pied bird is often called a clear pied and may be completely white.
Iridescence
Iridescent is a rare gene that adds a teal, cyan, blue and/or purple shiny glow to the bird's wings, especially visible and differing depending on the light. The iridescent gene is recessive.
| Allele | Phenotype | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| C | wild type | no change |
| ci | iridescent | iridescent effect across feathers |
The iridescent gene has a particularely different effect on each species of bird and each set of genes. Some species may only have iridescent patches around the neck or on the wings, while other species may show iridescent feathers all over the body. Iridescent feathers will be more noticable on dark colours.
























